SEO For Nonprofits: Using a Content Spreadsheet to Simplify Optimization
Elin Enrooth | August 2022

When creating content for your website, one of the most important things to consider is whether it will drive organic traffic. If it doesn’t, users won’t find it. Organic traffic is free and the more traffic a page receives, the higher it will rank in the search results. Creating (and updating) content is one of Google’s most prominent ranking factors. This means that publishing optimized content is one of the best ways to rank higher.
But, optimizing for SEO can be a monster of a project. Each page title, headers, and meta description need to be unique and include the right keywords. If so, users will be more inclined to click on your result. This benefits SEO as your click-through rate will increase.
Remember: no page titles, headers, or meta descriptions should match. Google flags these as duplicates and this will hurt your search rankings.
To ensure you’ve optimized each page for every component, create a content spreadsheet.
This spreadsheet should list every page on your site and include the:
- Page name
- URL
- Page title
- Keywords
- H1
- H2’s (only populate as necessary)
- Meta description
Copy this spreadsheet to your Google Drive to get started.
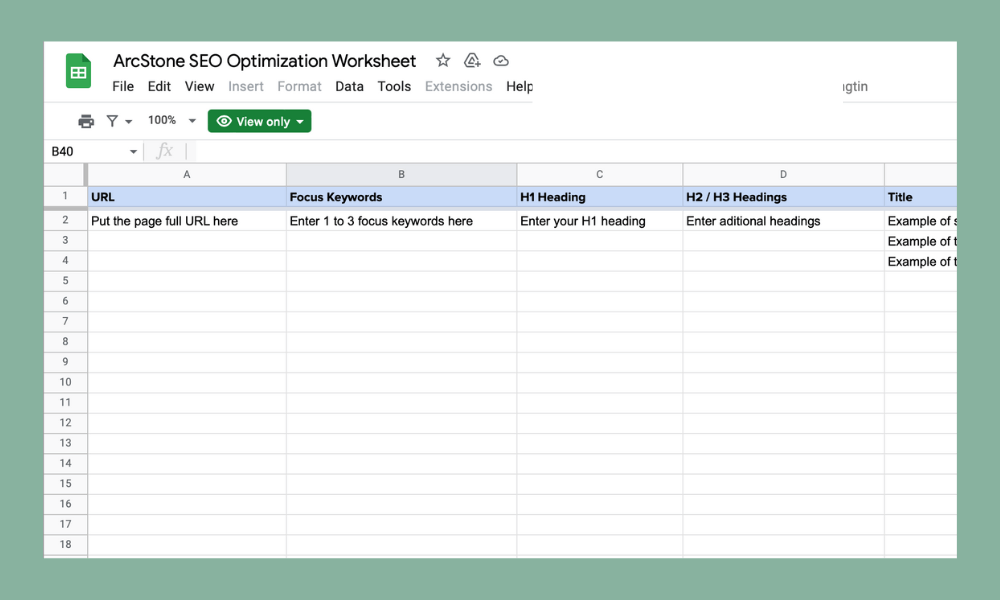
Using this spreadsheet to plan (or update) content will help optimize your site for search engines.
Page titles
A title tag, or page title, is an HTML element used to specify the title of a webpage. The title isn’t visible on the page itself, only on the browser tab. Its purpose is to tell both users and search engines what they can expect from the page. It also helps search engines decide how relevant a page is to a searcher’s query. Titles should be long enough to entice the reader, but short enough to make the meaning of the page clear. On both desktop and mobile devices, titles must be at least 30 characters long. But, Google only displays 60-70 characters of a page title in the results. If the title is longer than 70 characters, Google will truncate it and put an ellipsis in its place. Aim to make titles around 60 characters long.
Titles should be long enough to entice the reader, but short enough to make the meaning of the page clear. On both desktop and mobile devices, titles must be at least 30 characters long. But, Google only displays 60-70 characters of a page title in the results. If the title is longer than 70 characters, Google will truncate it and put an ellipsis in its place. Aim to make titles around 60 characters long. Every page of your website should be unique, and so should its title. Title tags should be as accurate and relevant to the page’s content as possible. Think about the specifics of the page and try to describe it.
Every page of your website should be unique, and so should its title. Title tags should be as accurate and relevant to the page’s content as possible. Think about the specifics of the page and try to describe it.
Because title tags show up in the SERPs, it’s also essential that they entice users to click-through. Start each title with the most logical keywords to summarize the page so that users are more likely to see them.
If your title isn’t specific, Google may rewrite it, which can reduce the click-through rate. Google rewrites title tags and meta descriptions when it doesn’t think that they will entice a click. Google’s goal is to connect users with the best content for their query. If it doesn’t think that the current tag communicates that, it will rewrite it.
A study by Zyppy analyzed more than 80,000 title tags to determine how many of them were used in search results. They discovered that Google rewrote 61.6 percent of the title tags.
This can be frustrating, especially when you’ve spent time crafting optimized tags. Unfortunately, you can’t stop Google from rewriting your title tags. You stand the best chance of keeping your title tag by crafting a great one in the first place. Make sure that it describes the content on your page and entices a click.
What keywords should each page be optimized for?
To be found by the right users, you have to make sure that your page ranks for the right keywords. To determine which keywords to optimize each page for, you must conduct research. We like to use Semrush, but Ahrefs and Moz are also great tools with free options.
Start by entering the URL of each page into the Semrush “Domain Overview” tab. Scroll down the page to see what each page is already ranking for. If this doesn’t match your intent, or the page isn’t ranking well, navigate to the Keyword Overview tool. Use this to determine the ranking difficulty of each keyword and discover new ideas.
When implementing your keywords, make sure to only include them when it’s natural.If a keyword doesn’t fit, then you shouldn’t optimize for that keyword.
Long ago, SEO experts practiced something called “keyword stuffing.” This was the practice of including keywords as many times as possible on a page to rank higher in the SERPs. But as Google’s technology has improved, it has cracked down on this practice and will actually flag pages written this way. Keyword-stuffed pages aren’t useful or pleasant for readers. Also, Google can now determine the topic of a page without needing to count as many keywords as possible.
Header tags
A header tag is a bit of HTML code that tells a web browser how to display the content of a webpage. Header tags separate headings and subheadings. They follow a hierarchy, from <h1> to <h6>. This hierarchy establishes a level of importance, which creates structure on a webpage.
- The H1 tag is the most important as it functions as the page title. It’s a critical ranking factor and tells search engines what a page is about. Google has said there is no problem with using more than one H1. But, that doesn’t mean it’s a best practice to do so.
- H2 tags are subheaders that divide the content into logical sections.
- H3 tags are subsections that further divide and clarify your content.
- H4, H5, and H6 tags are subsections that further organize content on the page. They allow you to add granular details and can be for formatting lists or bullet points.
Header tags tell both users and search engines what a page is about. Users rarely read an entire piece of content. So, headers help them scan the page. Each header should give the reader an idea of what each section contains. Search engines use headers to crawl a page and determine how to rank it. This helps Google serve relevant results.
Heading structure is also important for accessibility. Especially for people who can’t read from a screen. Because headings are in HTML, screen readers can understand the structure and read them out loud.
Since Google uses header tags to gather context for your page, it’s worth including keywords. But, we’re not talking about keyword stuffing. Only include keywords if they are relevant and meaningful to the content. Always think of your user first. Then, optimize for GoogleMeta descriptions
Meta descriptions are short descriptions of a page. They summarize the content you will find when you click on a link on the search engine results page (SERP). Poor or missing meta descriptions can result in lost traffic and low click-throughs. Meta descriptions must be at least 70 characters and no more than 155 on desktop and 130 on mobile devices. Google dedicates less space on mobile devices, as it results in more scrolling for the user. Short meta descriptions are easy to miss when people scan the search results. Long descriptions take up more space, pushing other pages further down the results. Like page titles, long meta descriptions will be truncated. Keep meta descriptions between 100-130 characters to make the best use of the space.
Meta descriptions must be at least 70 characters and no more than 155 on desktop and 130 on mobile devices. Google dedicates less space on mobile devices, as it results in more scrolling for the user. Short meta descriptions are easy to miss when people scan the search results. Long descriptions take up more space, pushing other pages further down the results. Like page titles, long meta descriptions will be truncated. Keep meta descriptions between 100-130 characters to make the best use of the space.
Each webpage should have a unique meta description that describes its content. The meta description serves as the “value prop” of the page. This is where you need to convince users to click. While the title grabs a user’s attention, the description communicates the value they’ll get from visiting the page. Include keywords to increase the chance that a user will spot the query they were looking for. As with page titles, don’t stuff keywords into the description. Instead, use the right keyword in the right place.
Page titles and meta descriptions work together to influence users to click. Because of this, both the title and description must complement each other. The better the title and description, the higher the click-through rate. So, even though improving these elements won’t have a direct affect on SEO, the effect of these changes will.
If you need help optimizing your website for search engines, reach out to the team at ArcStone. We offer an SEO audit conducted by in-house SEO experts. Our SEO audit dives into your website analytics, health, organic positioning, and more. We specialize in both technical and on-page SEO, providing a comprehensive strategy.
All SEO Audits Include:
- Indexation Check
- Tests for Site Health and Site Speed
- Backlink Profile Check
- Organic Positioning As Compared to Competitors
- Overview of Top Sources of Traffic
- Opportunities to Pair SEO Efforts With Content
- Audit of Google Analytics Setup / Data
- 90-day Priority Plan
SEO is ever changing and so is your website, so being aware of tried and true best practices is crucial. Our audits come with a best practices document to help you keep your site optimized. Contact us to schedule an SEO audit with one of our experts today!
